What Is The Difference Between THC-A And Delta 9
As cannabis becomes more widely accepted, people are exploring the diverse compounds within the plant. Among the well-known cannabinoids, THC-A (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and Delta 9 THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) are particularly notable. Although related, these two cannabinoids differ significantly in their properties, uses, and effects. Knowing the distinctions between THC-A and Delta 9 THC can empower consumers to make more informed choices, whether they seek cannabis for recreational enjoyment or medicinal relief.
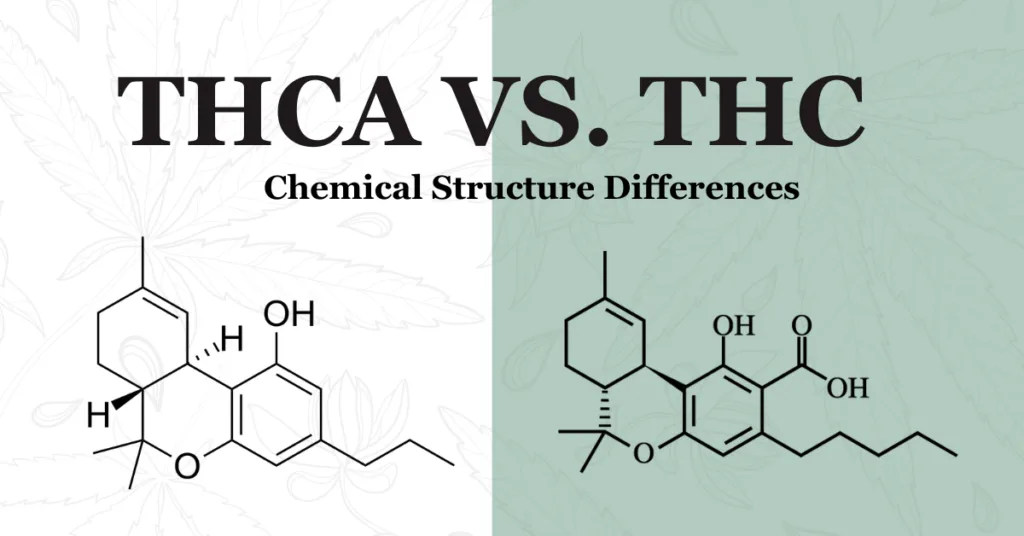
Chemical Structure and Composition
THC-A serves as the precursor to Delta 9 THC. In its raw state, cannabis is rich in THC-A, a non-psychoactive compound. However, THC-A converts into Delta 9 THC through decarboxylation, a heat-triggered process that occurs during smoking, vaping, or cooking. The heat removes the acid group from THC-A, transforming it into the psychoactive Delta 9 THC. Without this heating process, THC-A retains its original form and does not induce the “high” that Delta 9 THC is known for.
Chemically, THC-A and Delta 9 THC differ only by a carboxyl group (-COOH) present in THC-A but absent in Delta 9 THC. This subtle structural variation accounts for their distinct effects on the body.
Psychoactive Effects
One key difference between THC-A and Delta 9 THC lies in their psychoactive effects. In its raw state, THC-A is non-intoxicating, meaning it doesn’t produce the high typically associated with cannabis. Consuming raw cannabis through juicing or adding it to foods without heating won’t result in psychoactive effects.
This makes THC-A appealing to those who want to explore potential wellness benefits from cannabis without experiencing mind-altering effects.
Delta 9 THC: Psychoactive Effects and Experience
Delta 9 THC is widely recognized for its psychoactive properties. By binding to CB1 receptors in the brain, it produces the euphoric, mind-altering effects often linked to cannabis use. This compound is primarily responsible for the high that people experience when smoking, vaporizing, or consuming THC-infused products.
Health Benefits and Therapeutic Applications
While both THC-A and Delta 9 THC offer potential health benefits, they operate differently. THC-A is under study for its anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anti-nausea benefits. It appeals to those seeking therapeutic relief without the psychoactive effects, making it potentially beneficial for conditions like arthritis, autoimmune disorders, and some neurological issues, though further research is needed.
Delta 9 THC, with its psychoactive qualities, has been more extensively studied for pain relief, nausea reduction (especially in cancer patients on chemotherapy), and appetite stimulation in conditions like HIV/AIDS. It may also help reduce anxiety at lower doses, though higher doses can sometimes trigger anxiety. Delta 9 THC is used both recreationally and medicinally in areas where cannabis is legal.
Legal Status of THC-A and Delta 9 THC
The legality of THC-A and Delta 9 THC varies by region. Since THC-A does not produce psychoactive effects, it is often unregulated, allowing access to raw cannabis products in areas where Delta 9 THC is restricted. Delta 9 THC, due to its intoxicating properties, is more strictly regulated and remains a Schedule I substance at the federal level in the U.S., although individual states have passed varying laws for medical and recreational use. This distinction between THC-A and Delta 9 THC is important for consumers navigating differing cannabis laws.
Decarboxylation and Consumption Methods
Consumption methods play a key role in determining whether a person is ingesting THC-A or Delta 9 THC. Raw cannabis retains THC-A, allowing consumers to enjoy its potential benefits without the psychoactive effects when used in juices or salads, a method gaining popularity for its therapeutic appeal without intoxication. However, heating cannabis—by smoking, vaporizing, or cooking—causes decarboxylation, converting THC-A to Delta 9 THC, which activates the psychoactive effects sought by many recreational users.
The Entourage Effect
Both THC-A and Delta 9 THC contribute to the “entourage effect,” where cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids work together, amplifying each other’s therapeutic benefits. While THC-A does not cause intoxication alone, its presence in a broader cannabinoid profile may enhance the therapeutic potential of cannabis when combined with Delta 9 THC and other compounds.
Summary
THC-A and Delta 9 THC are closely related yet distinct cannabinoids that offer unique experiences. THC-A provides therapeutic benefits in its raw form without psychoactive effects, making it ideal for those seeking medicinal relief without the high. Delta 9 THC, known for its intoxicating properties, is used both medically and recreationally. Understanding these differences helps individuals make informed decisions on cannabis use, whether for health or enjoyment.





